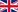
The Eurasian nuthatch or wood nuthatch (Sitta europaea) is a small passerine bird found throughout temperate Asia and in Europe, where its name is the nuthatch. Like other nuthatches, it is a short-tailed bird with a long bill, blue-grey upperparts and a black eye-stripe. It is a vocal bird with a repeated loud dwip call. There are more than 20 subspecies in three main groups; birds in the west of the range have orange-buff underparts and a white throat, those in Russia have whitish underparts, and those in the Far East have a similar appearance to European birds, but lack the white throat. The Eurasian nuthatch eats mainly insects, particularly caterpillar and beetles. In autumn and winter, the diet is supplemented with nuts and seeds, hazel nuts and beech mast being preferred. The young are fed mainly on the insects favoured by their parents, with some seeds. Food items are found mainly on tree trunks and large branches, but smaller branches may also be investigated, and food may be taken from the ground, especially outside the breeding season. Nuthatches can forage when descending trees head first, as well as when climbing. The adult male of the nominate subspecies, S. e. europaea is 14 cm (5.5 in) long with a 22.5–27 cm (8.9–10.6 in) wingspan.It weighs 17–28 g (0.6–1 oz). It has blue-grey upperparts, a black eye-stripe and whitish throat and underparts. The flanks and lower belly are orange-red, mottled with white on the undertail. The stout bill is dark grey with a paler area on the base of the lower mandible, the iris is dark brown and the legs and feet are pale brown or greyish.
(latin: Sitta europaea)