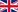
The western jackdaw (Coloeus monedula), also known as the Eurasian jackdaw, European jackdaw, or simply jackdaw, is a passerine bird in the crow family. Found across Europe, western Asia and North Africa, it is mostly resident, although northern and eastern populations migrate south in winter. Four subspecies are recognised, which mainly differ in the colouration of the plumage on the head and nape. Linnaeus first described it formally, giving it the name Corvus monedula. The common name derives from the word jack, denoting "small", and daw, a less common synonym for "jackdaw", and the native English name for the bird.
Measuring 34–39 centimetres (13–15 in) in length, the western jackdaw is a black-plumaged bird with a grey nape and distinctive pale-grey irises. It is gregarious and vocal, living in small groups with a complex social structure in farmland, open woodland, on coastal cliffs, and in urban settings. Like its relatives, jackdaws are intelligent birds, and have been observed using tools. An omnivorous and opportunistic feeder, it eats a wide variety of plant material and invertebrates, as well as food waste from urban areas. Western jackdaws are monogamous and build simple nests of sticks in cavities in trees, cliffs, or buildings. About five pale blue or blue-green eggs with brown speckles are laid and incubated by the female. The young fledge in four to five weeks.
Measuring 34–39 centimetres (13–15 in) in length, the western jackdaw is the second smallest member of the genus Corvus. Most of the plumage is a shiny black, with a purple (in subspecies monedula and spermologus) or blue (in subspecies cirtensis and soemmerringii) sheen on the crown, forehead, and secondaries, and a green-blue sheen on the throat, primaries, and tail. The cheeks, nape and neck are light grey to greyish-silver, and the underparts are slate-grey. Western jackdaws inhabit wooded steppes, pastures, cultivated land, coastal cliffs, and towns. They thrive when forested areas are cleared and converted to fields and open areas. Habitats with a mix of large trees, buildings, and open ground are preferred; open fields are left to the rook, and more wooded areas to the Eurasian jay.
(latin: Coloeus monedula)