A bumblebee (or bumble bee, bumble-bee, or humble-bee) is any of over 250 species in the genus Bombus, part of Apidae, one of the bee families. This genus is the only extant group in the tribe Bombini, though a few extinct related genera (e.g., Calyptapis) are known from fossils. They are found primarily in higher altitudes or latitudes in the Northern Hemisphere, although they are also found in South America where a few lowland tropical species have been identified. European bumblebees have also been introduced to New Zealand and Tasmania. Female bumblebees can sting repeatedly, but generally ignore humans and other animals.
Most bumblebees are social insects that form colonies with a single queen. The colonies are smaller than those of honey bees, growing to as few as 50 individuals in a nest. Cuckoo bumblebees are brood parasitic and do not make nests; their queens aggressively invade the nests of other bumblebee species, kill the resident queens and then lay their own eggs, which are cared for by the resident workers. Cuckoo bumblebees were previously classified as a separate genus, but are now usually treated as members of Bombus.
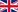
Bumblebees have round bodies covered in soft hair (long branched setae) called pile, making them appear and feel fuzzy. They have aposematic (warning) coloration, often consisting of contrasting bands of colour, and different species of bumblebee in a region often resemble each other in mutually protective Müllerian mimicry. Harmless insects such as hoverflies often derive protection from resembling bumblebees, in Batesian mimicry, and may be confused with them. Nest-making bumblebees can be distinguished from similarly large, fuzzy cuckoo bees by the form of the female hind leg. In nesting bumblebees, it is modified to form a pollen basket, a bare shiny area surrounded by a fringe of hairs used to transport pollen, whereas in cuckoo bees, the hind leg is hairy all round, and pollen grains are wedged among the hairs for transport.
Like their relatives the honeybees, bumblebees feed on nectar, using their long hairy tongues to lap up the liquid; the proboscis is folded under the head during flight. Bumblebees gather nectar to add to the stores in the nest, and pollen to feed their young. They forage using colour and spatial relationships to identify flowers to feed from. Some bumblebees steal nectar, making a hole near the base of a flower to access the nectar while avoiding pollen transfer. Bumblebees are important agricultural pollinators, so their decline in Europe, North America, and Asia is a cause for concern. The decline has been caused by habitat loss, the mechanisation of agriculture, and pesticides.
(Latin: Bombus terrestris)